Global Financial Data has added data on individual stocks from the Copenhagen stock market between 1871 and 1937 to the database. This provides a history of Danish stocks that was previously unavailable. In the midst of putting together this data, we discovered a forgotten stock market bubble of shipping stocks during World War I.
This bubble followed the classic pattern of a dramatic rise followed by a crash, but we have never seen this bubble mentioned in any of the sources we have consulted. In many ways, this was a “rational” bubble since dividends paid by the shipping companies rose dramatically during World War I and then collapsed after the war. The details of this bubble are discussed below.
Data Sources
Global Financial Data went to a number of sources in order to put together 65 years of history on the Danish stock market. Theodor Green published Fonds og Aktier beginning in 1883 and periodically in the years that followed. The books provided price data for Danish stocks as well as shares outstanding and dividend data. In 1893, Danmarks Statistik began providing data on individual stocks and dividends of individual companies in its Statistisk Aarbog, and continued to provide this data until 1937.
Danmarks Statistik began calculating its own index of Danish stock prices after World War I, so collecting and organizing this data enables us to put together an index of Danish stock prices going back 45 years before the Danish index was calculated. Global Financial Data has put together a database of almost 100 companies to create Danish indices that previously did not exist. With this data, GFD has calculated a cap-weighted price index and return index as well as the dividend yield on Danish stocks between 1871 and 1937.
The graph above shows the price and total returns to stocks in Denmark from 1873 to 1937. As is quite obvious, the price of Danish stocks hardly budged during those 60 years. The average price of stocks generally rose between 1878 and 1898, but then, with the exception of the bubble during World War I, declined for the next 40 years. 1 Krone invested in Danish stocks in 1871 grew to 1.3 Krone by 1937, an annual return of 0.4%.
All of the return came in the dividends that were paid to shareholders. Allowing for the reinvestment of dividends, 1 Krone invested in the Danish stock market in 1871 grew to 50 Krone by 1937, an annual return of 6.1%, implying an average dividend yield of 5.7%.
As the chart above shows, Danish stocks paid a dividend that ranged between 4 percent and 6 percent during those 65 years. The exception to this rule was the period during World War I when the dividend yield rose to 8 to 10 percent per annum. The higher yield occurred despite the strong rise in the prices of Danish shipping stocks. Without the reinvestment of dividends, Danish shareholders would have had little to show for their investment.
The Forgotten Bubble
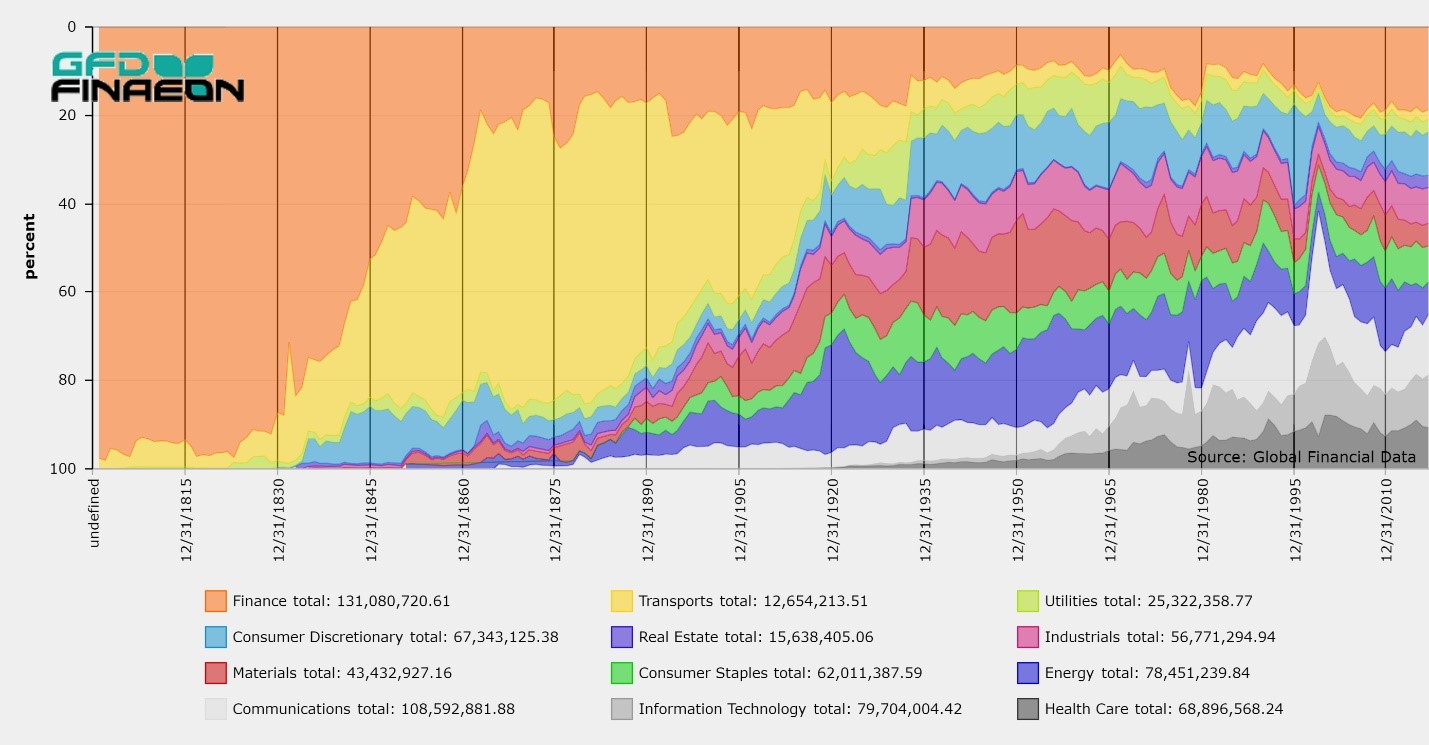
Danish shipping stocks were an important part of the Danish stock market, but overall represented a small portion of the total stock market capitalization. As the chart below shows, transports represented around 10% of the Danish stock market. The two primary sectors on the Copenhagen stock exchange were banks and telecommunications. The banks were represented by Denmark’s four main banks, the Nationalbank, the Privatbank, the Landmandsbank and the Handelbank. The Great Northern Telegraph Co., which listed on the London Stock Exchange, was the largest company in Denmark, representing from 20 to 30 percent of the Danish stock market’s capitalization.
It should be remembered that because Denmark is largely a collection of islands and peninsulas, railroads never played a major role in the Danish economy. There were private tramways in the main cities, but they were eventually nationalized by the government. Almost all the transport companies in Denmark were shipping companies and the largest of these was the United Steamship Co. (Forenede Dampskibsselskabs A/S).
If you look at the Sector Stacked Graph below, the bubble in transport stocks between 1914 and 1921 sticks out like a sore thumb. Shipping revenues and profits rose dramatically during World War I, leading to higher dividends and higher stock prices. Just to use the United Steamship Co. as an example, the company’s dividend rose from 8% in 1914 to 60% in 1919 then collapsed to 5% by 1922. Other steamship companies provided even more dramatic changes.
The odd thing is the bubble of 1915 to 1918 has gone virtually unnoticed. It even fails to be mentioned in Charles P. Kindleberger’s Manias, Panics and Crashes. Why did the stock market bubble occur, and why was it forgotten?
The most likely reason this bubble has been forgotten is that Denmark is a small country and the bubble occurred in the midst of World War I when much more important events overshadowed the performance of the stock market in a small, neutral country. Since no stock market index existed in Denmark at the time, there was no chart of the bubble until now.
Denmark in World War I
Denmark was in a difficult position when World War I began. Denmark was a neutral country even before the onset of the war. Denmark had been defeated in 1864 in its war with Prussia. After the war, Denmark lost the territory of Northern Schleswig, which had a majority Danish population, to Prussia and even though Denmark would have liked to regain control over Northern Schleswig, the political reality was that Denmark was too small to challenge Prussia politically or economically. Consequently, neutrality became a part of the Danish mentality.
Before World War I, Denmark was highly dependent on imports and exports with ninety percent of exports derived from agriculture in 1913. Denmark built up a large shipping fleet that carried 70% of its shipping between foreign ports. Denmark’s shipping industry was as large as Spain’s, and it was the fourteenth largest merchant marine in the world when World War I began. The Danish merchant marine’s net tonnage doubled in size between 1885 and 1914, and most of this investment was in more efficient steam shipping and motor vessels.
The Danish shipping industry was dominated by Det Forenede Dampskib-selskab (United Steamship Company of Copenhagen, now known as DFDS) which represented three-eighths of Danish shipping in 1914. The company was founded on December 11, 1866 when Carl Frederik Tietgen merged the three largest steamship companies into a single company. Since its founding in 1866, the company has consistently paid a dividend over 7% reflecting the profitability of the company and the sector.
Denmark was officially neutral during World War I, but leaned toward Germany for obvious political reasons, laying mine fields around its waters to control the Baltic states at Germany’s request. Laying down and keeping track of errant mines was the Danish navy’s main job during the war. With the onset of World War I, the riskiness of shipping increased, raising insurance costs. Denmark’s government helped to alleviate these costs by covering three-fourths of the risk to the Danish merchant marine. The risk was real since Denmark lost 324 ships and 702 seamen during World War I.
Nevertheless, Denmark’s neutrality worked to its advantage since it could trade with Germany, Britain and all the countries involved in the war. Between 1914 and 1917, the Danish economy boomed as businesses took advantage of Denmark’s opportunities. The result was not only a growing economy, but stock market speculation, especially in shipping companies.
The profits were reflected in the dramatic increase in dividends the shipping companies paid. The United Shipping Co. had paid a dividend of 8% in 1914 and 60% in 1919. The Neptune Steamship company’s dividend increased from 12% in 1914 to 135% in 1919. The Gorm Steamship Co.’s dividend increased from 10% in 1914 to 100% in 1916. Similar dividend increases occurred for other shipping companies.
During the same period of time, the dividends paid by firms in other sectors barely budged. The dividend paid by Royal Marine Insurance Co. doubled, but the dividend paid by the General Fire Insurance Partnership remained unchanged. The dividends paid by the National Bank of Denmark and Great Northern Telegraph Co. didn’t change at all during World War I.
As the chart below shows, GFD’s index of Danish Shipping shares increased six-fold between 1914 and the end of 1916. On February 1, 1917, Germany issued its declaration of unrestricted submarine warfare, and shipping stocks lost one-third of their value. The United States issued an export ban to Denmark and in October 1917, Britain stopped all exports to Denmark, except for coal. Denmark replaced the British and American trade with greater reliance on other Scandinavian countries and Germany, a substitute which worked successfully for the rest of the war.
With the conclusion of the war, Denmark was not only able to carry goods to Scandinavia and Germany, but to Britain and to the United States, which had concluded a trade agreement with Denmark in September 1918. Share prices surged again, rising above the peaks of 1916.
Unfortunately, World War I was followed by a depression between 1920 and 1921. The demand for Danish shipping services collapsed as did the dividends the companies paid. The United Steamship Co.’s dividend fell from 60% in 1919 to 5% in 1922. The Neptune Steamship’s dividend fell from 135% in 1919 to 10% in 1922.
United Steamship shares traded at 107.5 in July 1914, rose to 515 in February 1920, and fell to 129 in May 1921. By the end of 1932, United Steamship shares were trading at 30, substantially below where they had been before World War I.
If you adjust for inflation, you can see that the Danish stock market suffered an 80-year bear market between 1898 and 1980. Because Denmark suffered from inflation during World War I and economic depression after World War I, most shareholders suffered dearly during the first 30 years of the 1900s. Only during the past 35 years have Danish stocks consistently provided strong real returns to shareholders.
Conclusion
The Danish Shipping Stock Market bubble of 1914-1920 has long been forgotten, but is a dramatic reminder of how war, politics and the economy affect the stock market. Denmark’s unique geographical and political situation during World War I enabled it to profit from the changes that occurred during the war. The profits were concentrated in the shipping industry and it alone benefitted from the war while the rest of the economy reaped few benefits.
The price increases the shipping stocks enjoyed were justified by the dramatic increase in profits and dividends that occurred. In some cases, profits and dividends increased ten-fold during the war and prices responded accordingly. When the war was over and depression followed, share prices collapsed. By any stretch of the imagination, it was a “rational” bubble.
The data for the Copenhagen stock exchange, both the data for the individual companies and the GFD Indices that were calculated based upon those indices are available to all subscribers to the stock database. If you would like to access this data and currently do not have access, please feel free to call one of our sales representatives at 877-DATA-999 or 949-542-4200.
 Global Financial Data has added data on individual stocks from the Copenhagen stock market between 1871 and 1937 to the database. This provides a history of Danish stocks that was previously unavailable. In the midst of putting together this data, we discovered a forgotten stock market bubble of shipping stocks during World War I.
This bubble followed the classic pattern of a dramatic rise followed by a crash, but we have never seen this bubble mentioned in any of the sources we have consulted. In many ways, this was a “rational” bubble since dividends paid by the shipping companies rose dramatically during World War I and then collapsed after the war. The details of this bubble are discussed below.
Global Financial Data has added data on individual stocks from the Copenhagen stock market between 1871 and 1937 to the database. This provides a history of Danish stocks that was previously unavailable. In the midst of putting together this data, we discovered a forgotten stock market bubble of shipping stocks during World War I.
This bubble followed the classic pattern of a dramatic rise followed by a crash, but we have never seen this bubble mentioned in any of the sources we have consulted. In many ways, this was a “rational” bubble since dividends paid by the shipping companies rose dramatically during World War I and then collapsed after the war. The details of this bubble are discussed below.